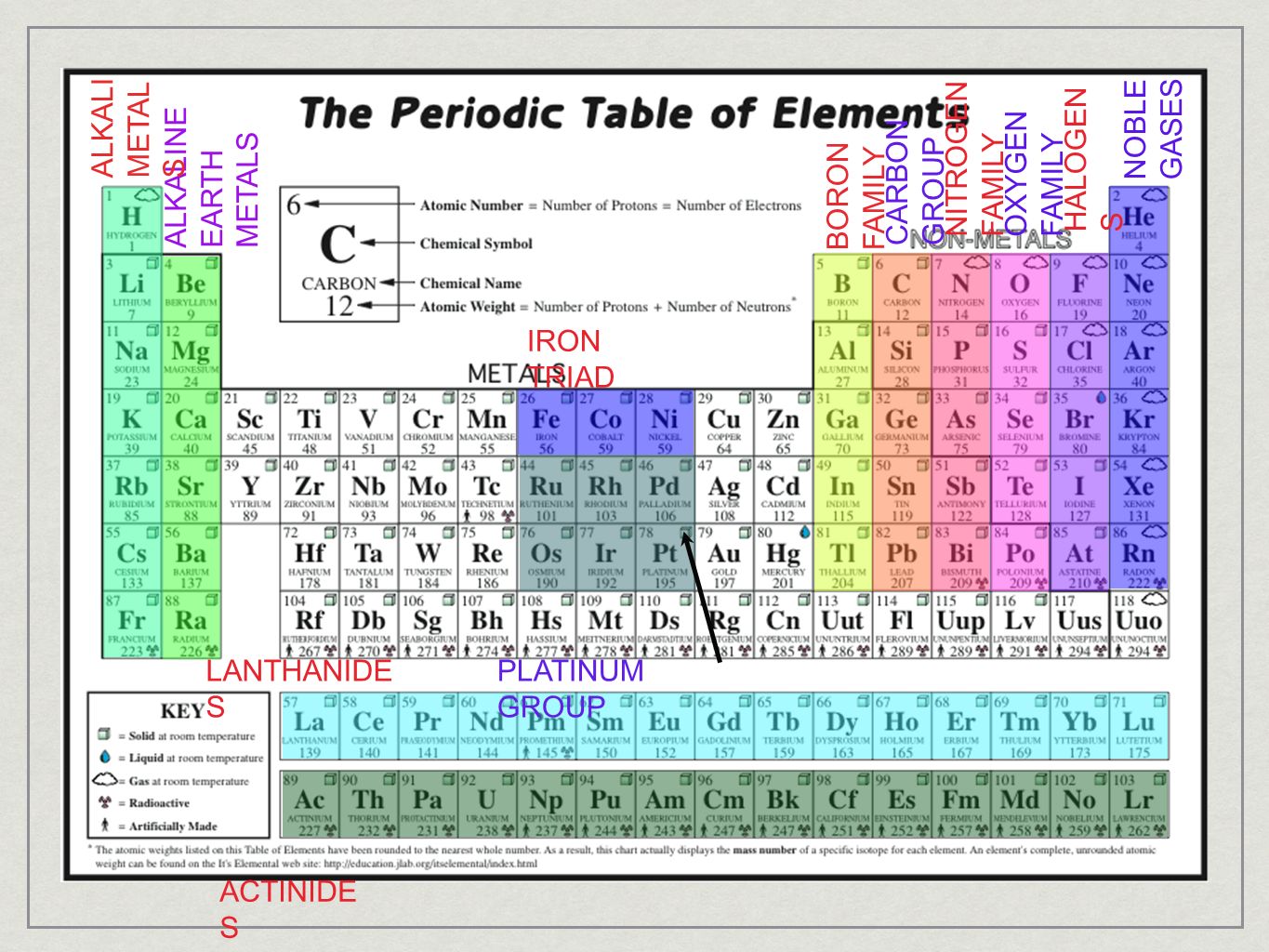
What happens at the anode
What Happens At The Anode. At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. The anode may be a source of positive charge or an electron acceptor. The anode attracts electrons or anions.
 Electrolysis Copper Sulfate Solution With Copper Carbon Graphite Electrodes Electroplating Half Equations Products Anode Cathode Apparatus Electrolyte Cell Gcse Chemistry Ks4 Science Igcse O Level Revision Notes From docbrown.info
Electrolysis Copper Sulfate Solution With Copper Carbon Graphite Electrodes Electroplating Half Equations Products Anode Cathode Apparatus Electrolyte Cell Gcse Chemistry Ks4 Science Igcse O Level Revision Notes From docbrown.info
The anode attracts electrons or anions. At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being. The anode is the positively charged electrode. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit.
In electrochemistry the anode is where oxidation occurs and is the positive polarity contact in an electrolytic cell.
The anode may be a source of positive charge or an electron acceptor. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. The anode may be a source of positive charge or an electron acceptor. At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct.
 Source: docbrown.info
Source: docbrown.info
Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. In electrochemistry the anode is where oxidation occurs and is the positive polarity contact in an electrolytic cell. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being.
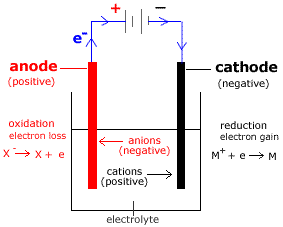 Source: minichemistry.com
Source: minichemistry.com
These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. The anode attracts electrons or anions.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. The anode is the positively charged electrode. In electrochemistry the anode is where oxidation occurs and is the positive polarity contact in an electrolytic cell. The anode attracts electrons or anions. Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being. The anode attracts electrons or anions. At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. The anode is the positively charged electrode. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. The anode attracts electrons or anions. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons.
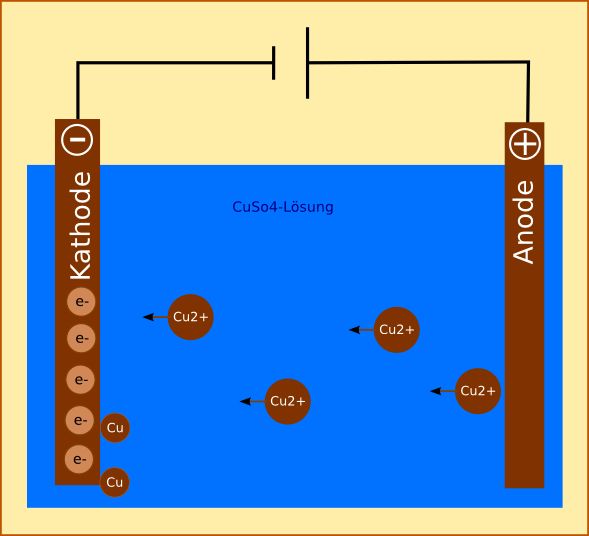 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. The anode attracts electrons or anions.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. The anode is the positively charged electrode. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction.
 Source: enotes.com
Source: enotes.com
The anode attracts electrons or anions. The anode attracts electrons or anions. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction.
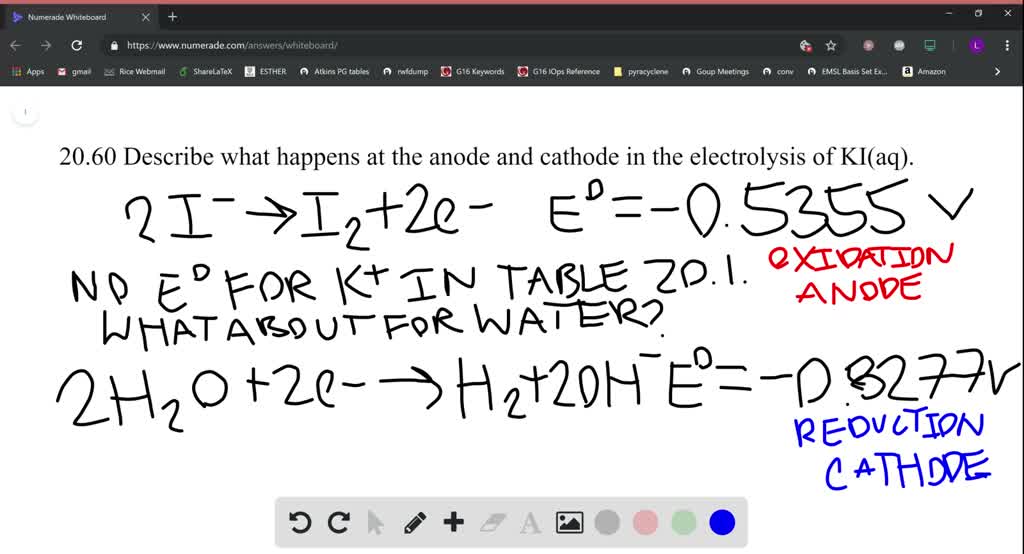 Source: numerade.com
Source: numerade.com
At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. The anode attracts electrons or anions. The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. The anode attracts electrons or anions. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The substance being oxidized is losing electrons and those electrons are gained by the substance being. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. Generally at an anode negative ions or anions due to its electrical potential tend to react and give off electrons.
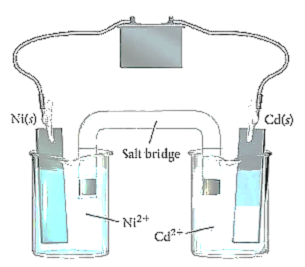 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
In electrochemistry the anode is where oxidation occurs and is the positive polarity contact in an electrolytic cell. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. The anode converts the energy of incident electrons into x rays dissipating heat as a byproduct. If we take a galvanic cell the anode is negative in nature and the electrons mostly move towards the external part of the circuit. At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit.
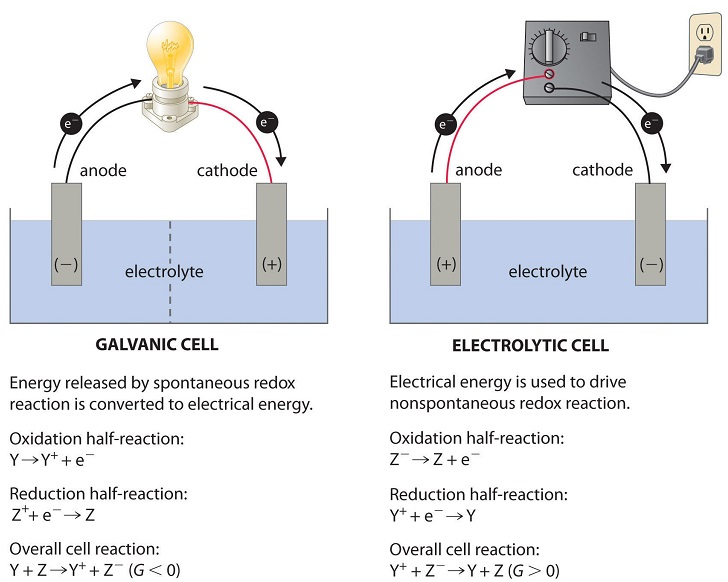 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
At the anode anions negative ions are forced by the electrical potential to react chemically and give off electrons oxidation which then flow up and into the driving circuit. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. The anode is the positively charged electrode. In electrochemistry the anode is where oxidation occurs and is the positive polarity contact in an electrolytic cell. The anode may be a source of positive charge or an electron acceptor.
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Most x ray tube anodes are made of tungsten the target material. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. The anode is the positively charged electrode. These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
These electrons then move up and into the driving circuit. The anode may be a source of positive charge or an electron acceptor. A chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred is called oxidation reduction. Tungsten has a high atomic number z 74 and a high melting point of 3370 c with a correspondingly low rate of evaporation. The anode attracts electrons or anions.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what happens at the anode by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.