The three laws of physics
The Three Laws Of Physics. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. True under specified conditions universal and do not deviate anywhere in the universe. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. The third law states that when a force acts on.
 Newton S Laws Of Motion 8th Grade Science From clarkscience8.weebly.com
Newton S Laws Of Motion 8th Grade Science From clarkscience8.weebly.com
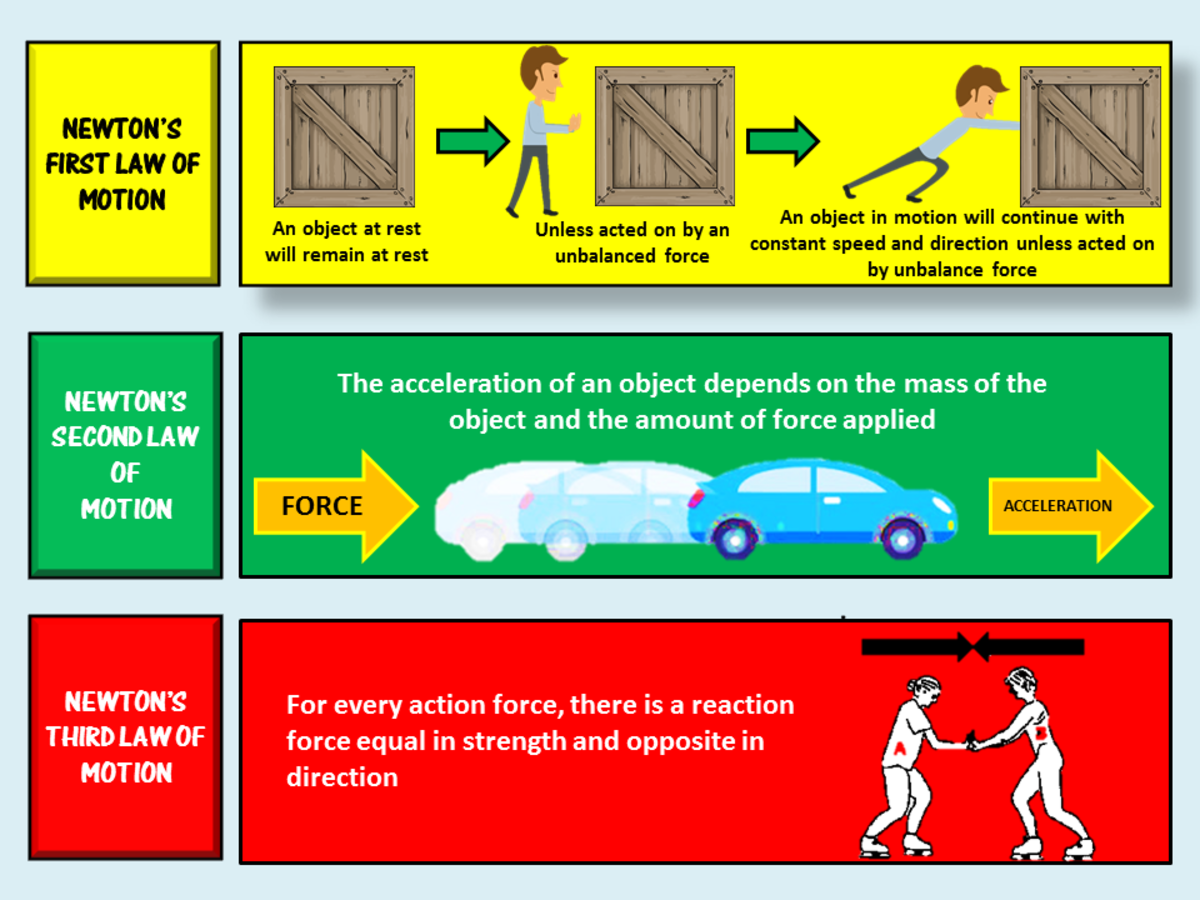
The different properties of laws of physics which shed information about their nature are given below. The third law states that when a force acts on. Sometimes in modern physics a more sophisticated approach is taken that incorporates elements of the three areas listed above. A particle not subjected to external forces remains at rest or moves with constant speed in a straight line. Newton s second law the law of force and acceleration the net external force acting on an object is equal to its mass times acceleration such that f m a. This law is important in analyzing problems of static equilibrium where all forces are balanced but it also applies to bodies in uniform or accelerated motion.
This law is important in analyzing problems of static equilibrium where all forces are balanced but it also applies to bodies in uniform or accelerated motion.
Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. Newton s first law the law of inertia an object at rest or at constant velocity stays in that state unless acted on by a net external force. The third law is also known as the law of action and reaction. The third law of thermodynamics states that it is impossible to create a thermodynamic process that is perfectly efficient. This law is important in analyzing problems of static equilibrium where all forces are balanced but it also applies to bodies in uniform or accelerated motion. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In classical mechanics newton s laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. Newton s second law the law of force and acceleration the net external force acting on an object is equal to its mass times acceleration such that f m a. They are stated as follows. The first law states that an object either remains at rest or continues to move at a constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an external force.
 Source: behavioraleconomics.com
Source: behavioraleconomics.com
The second law of thermodynamics relates to the natural flow of heat within a closed system. Newton s second law the law of force and acceleration the net external force acting on an object is equal to its mass times acceleration such that f m a. Newton s first law the law of inertia an object at rest or at constant velocity stays in that state unless acted on by a net external force. The different properties of laws of physics which shed information about their nature are given below. The three laws are as follows.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The third law states that when a force acts on. In classical mechanics newton s laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. The first law states that a body remains at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. General physics three laws of mechanics describing the motion of a body. Newton s laws of motion.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. The forces it describes are real ones not mere bookkeeping devices. The three laws are given as. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. The second law of thermodynamics relates to the natural flow of heat within a closed system.
 Source: owlcation.com
Source: owlcation.com
A particle not subjected to external forces remains at rest or moves with constant speed in a straight line. The forces it describes are real ones not mere bookkeeping devices. The three laws are as follows. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. True under specified conditions universal and do not deviate anywhere in the universe.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Newton s laws of motion. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. The first law states that a body remains at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force. They are stated as follows. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws.
 Source: survivalsherpa.wordpress.com
Source: survivalsherpa.wordpress.com
General physics three laws of mechanics describing the motion of a body. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws. The first law of thermodynamics demonstrates the relationship between internal energy added heat and work within a system. Newton s laws of motion. The third law is also known as the law of action and reaction.

True under specified conditions universal and do not deviate anywhere in the universe. The first rule states that an object will remain at rest or in a uniform state of motion unless that state is changed by an external force. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. The third law states that when a force acts on. The three laws are given as.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The second law of thermodynamics relates to the natural flow of heat within a closed system. The second law of thermodynamics relates to the natural flow of heat within a closed system. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. The first law of thermodynamics demonstrates the relationship between internal energy added heat and work within a system. The different properties of laws of physics which shed information about their nature are given below.
 Source: footballphysics24.weebly.com
Source: footballphysics24.weebly.com
The second law states that a body s rate of change of momentum is proportional to the force causing it. It relates to the laws of symmetry and conservation such as those pertaining to energy momentum charge and parity. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. Sometimes in modern physics a more sophisticated approach is taken that incorporates elements of the three areas listed above.
 Source: physicsabout.com
Source: physicsabout.com
Newton s laws of motion. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws. Newton s first law the law of inertia an object at rest or at constant velocity stays in that state unless acted on by a net external force. Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. The first law states that a body remains at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by a force.
 Source: teachengineering.org
Source: teachengineering.org
Three fundamental principles which form the basis of classical or newtonian mechanics. It relates to the laws of symmetry and conservation such as those pertaining to energy momentum charge and parity. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. Newton s second law the law of force and acceleration the net external force acting on an object is equal to its mass times acceleration such that f m a. The forces it describes are real ones not mere bookkeeping devices.
 Source: jagranjosh.com
Source: jagranjosh.com
The third law is also known as the law of action and reaction. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of an object is directly. The second law states that a body s rate of change of momentum is proportional to the force causing it. The three laws are given as. The second law of thermodynamics relates to the natural flow of heat within a closed system.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Sometimes in modern physics a more sophisticated approach is taken that incorporates elements of the three areas listed above. The third law of thermodynamics states that it is impossible to create a thermodynamic process that is perfectly efficient. General physics three laws of mechanics describing the motion of a body. This law is important in analyzing problems of static equilibrium where all forces are balanced but it also applies to bodies in uniform or accelerated motion. Newton s laws of motion.
 Source: clarkscience8.weebly.com
Source: clarkscience8.weebly.com
The first law states that an object either remains at rest or continues to move at a constant velocity unless it is acted upon by an external force. Newton laws gravitational law pascal law ohm s law faraday law lenz s law ampere s law joules law hook s law are basic physics laws. The first law of thermodynamics demonstrates the relationship between internal energy added heat and work within a system. The first rule states that an object will remain at rest or in a uniform state of motion unless that state is changed by an external force. The third law of thermodynamics states that it is impossible to create a thermodynamic process that is perfectly efficient.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title the three laws of physics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





