The energy of sound in air eventually becomes
The Energy Of Sound In Air Eventually Becomes. Energy is neither created nor destroyed. As explained elsewhere all of this energy eventually becomes low grade energy from friction and from heat rejected by the engine. It simply become another form of energy. What you hear is of course sound reflection better known as an echo.
 Chapter 17 Change Of Phase Pdf Free Download From docplayer.net
Chapter 17 Change Of Phase Pdf Free Download From docplayer.net
The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate. The frequencies of sound that carry farther in air are. The object with the highest natural frequency is a. Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations as they travel through air water or any other space. When these pressure waves reach the ear the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus pressure wave into a nerve impulse electrical signal that the brain perceives as sound. In physics a shock wave also spelled shockwave or shock is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium.
Like an ordinary wave a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt nearly discontinuous change in pressure temperature and density of the medium.
The human ear is an astounding transducer converting sound energy to mechanical energy to a nerve impulse that is transmitted to the brain. C cancelled by destructive interference. There s a delay between the sound and the echo because it takes time for the sound to race to the wall and back the bigger the distance the longer the delay. As explained elsewhere all of this energy eventually becomes low grade energy from friction and from heat rejected by the engine. Sound 21 the energy of sound in air eventually becomes a increased internal energy of the air. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm.
 Source: explainthatstuff.com
Source: explainthatstuff.com
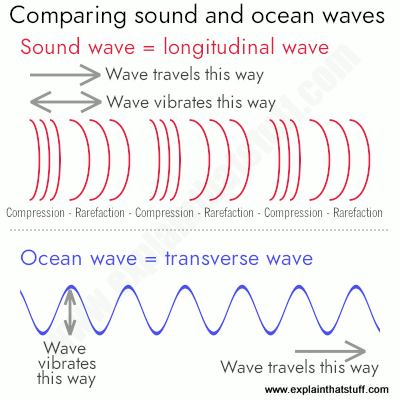
There s a delay between the sound and the echo because it takes time for the sound to race to the wall and back the bigger the distance the longer the delay. The ear s ability to do this allows us to perceive the pitch of sounds by detection of the wave s frequencies the loudness of sound by detection of the wave s amplitude and the timbre of the sound by the detection of the various frequencies that make up. These vibrations cause waves of pressure that from a physics standpoint lead to some level of compression and rarefaction. Energy is neither created nor destroyed. Like an ordinary wave a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt nearly discontinuous change in pressure temperature and density of the medium.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
Vibrating objects such as vocal cords create sound waves or pressure waves in the air. Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations as they travel through air water or any other space. While the air is necessary for the sound to travel any. It simply become another form of energy. Energy is neither created nor destroyed.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate. Eventually the energy is radiated back out into space. While the air is necessary for the sound to travel any. Like an ordinary wave a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt nearly discontinuous change in pressure temperature and density of the medium. The frequencies of sound that carry farther in air are.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The object with the highest natural frequency is a. As explained elsewhere all of this energy eventually becomes low grade energy from friction and from heat rejected by the engine. When these pressure waves reach the ear the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus pressure wave into a nerve impulse electrical signal that the brain perceives as sound. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm. The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate.
Source:
Like an ordinary wave a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium but is characterized by an abrupt nearly discontinuous change in pressure temperature and density of the medium. There s a delay between the sound and the echo because it takes time for the sound to race to the wall and back the bigger the distance the longer the delay. Vibrating objects such as vocal cords create sound waves or pressure waves in the air. Energy is neither created nor destroyed. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm.
 Source: docplayer.net
Source: docplayer.net
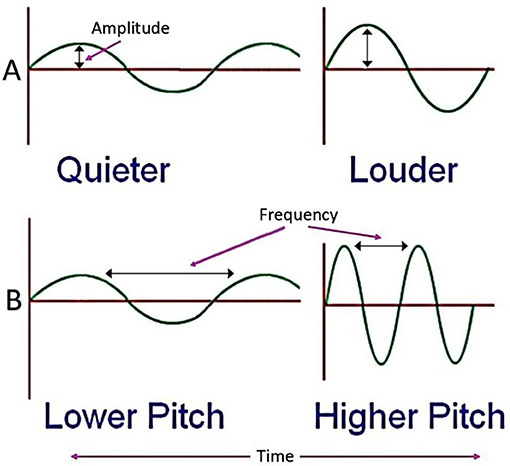
When these pressure waves reach the ear the ear transduces this mechanical stimulus pressure wave into a nerve impulse electrical signal that the brain perceives as sound. What you hear is of course sound reflection better known as an echo. Eventually the energy is radiated back out into space. Increased internal energy of the air. The ear s ability to do this allows us to perceive the pitch of sounds by detection of the wave s frequencies the loudness of sound by detection of the wave s amplitude and the timbre of the sound by the detection of the various frequencies that make up.
Source:
The frequencies of sound that carry farther in air are. The energy of sound in air eventually becomes a cancelled by destructive interference b increased internal energy of the air c weaker and weaker until it disappears d canceled by both destructive and constructive interference. It simply become another form of energy. What you hear is of course sound reflection better known as an echo. These vibrations cause waves of pressure that from a physics standpoint lead to some level of compression and rarefaction.
 Source: le.ac.uk
Source: le.ac.uk
The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate. It s the sound energy in your clap traveling out to the wall bouncing back and eventually entering your ears. This raises the surrounding air temperature a little bit. Increased internal energy of the air. Medium that is made up of molecules will.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Sound 21 the energy of sound in air eventually becomes a increased internal energy of the air. This raises the surrounding air temperature a little bit. There s a delay between the sound and the echo because it takes time for the sound to race to the wall and back the bigger the distance the longer the delay. Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations as they travel through air water or any other space. While the air is necessary for the sound to travel any.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations as they travel through air water or any other space. B weaker and weaker until it disappears. Sound energy is the energy produced by sound vibrations as they travel through air water or any other space. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm. C cancelled by destructive interference.
 Source: coursehero.com
Source: coursehero.com
In physics a shock wave also spelled shockwave or shock is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. C cancelled by destructive interference. It s the sound energy in your clap traveling out to the wall bouncing back and eventually entering your ears. Vibrating objects such as vocal cords create sound waves or pressure waves in the air. The object with the highest natural frequency is a.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
In other words they amplify bounce and move as they travel from their origin to people or animal ears which translate them into noise of varying levels. The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate. It simply become another form of energy. The energy of sound in air eventually becomes a cancelled by destructive interference b increased internal energy of the air c weaker and weaker until it disappears d canceled by both destructive and constructive interference. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm.

The pressure waves strike the tympanum causing it to vibrate. Energy is neither created nor destroyed. These vibrations cause waves of pressure that from a physics standpoint lead to some level of compression and rarefaction. The object with the highest natural frequency is a. Eventually the energy is radiated back out into space.
Source:
Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm. It s the sound energy in your clap traveling out to the wall bouncing back and eventually entering your ears. It simply become another form of energy. B weaker and weaker until it disappears. Medium that is made up of molecules will.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Energy is neither created nor destroyed. C cancelled by destructive interference. In other words they amplify bounce and move as they travel from their origin to people or animal ears which translate them into noise of varying levels. Sound 13 sound travels faster in air if the air temperature is a warm. Vibrating objects such as vocal cords create sound waves or pressure waves in the air.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title the energy of sound in air eventually becomes by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.