Properties of polar molecules
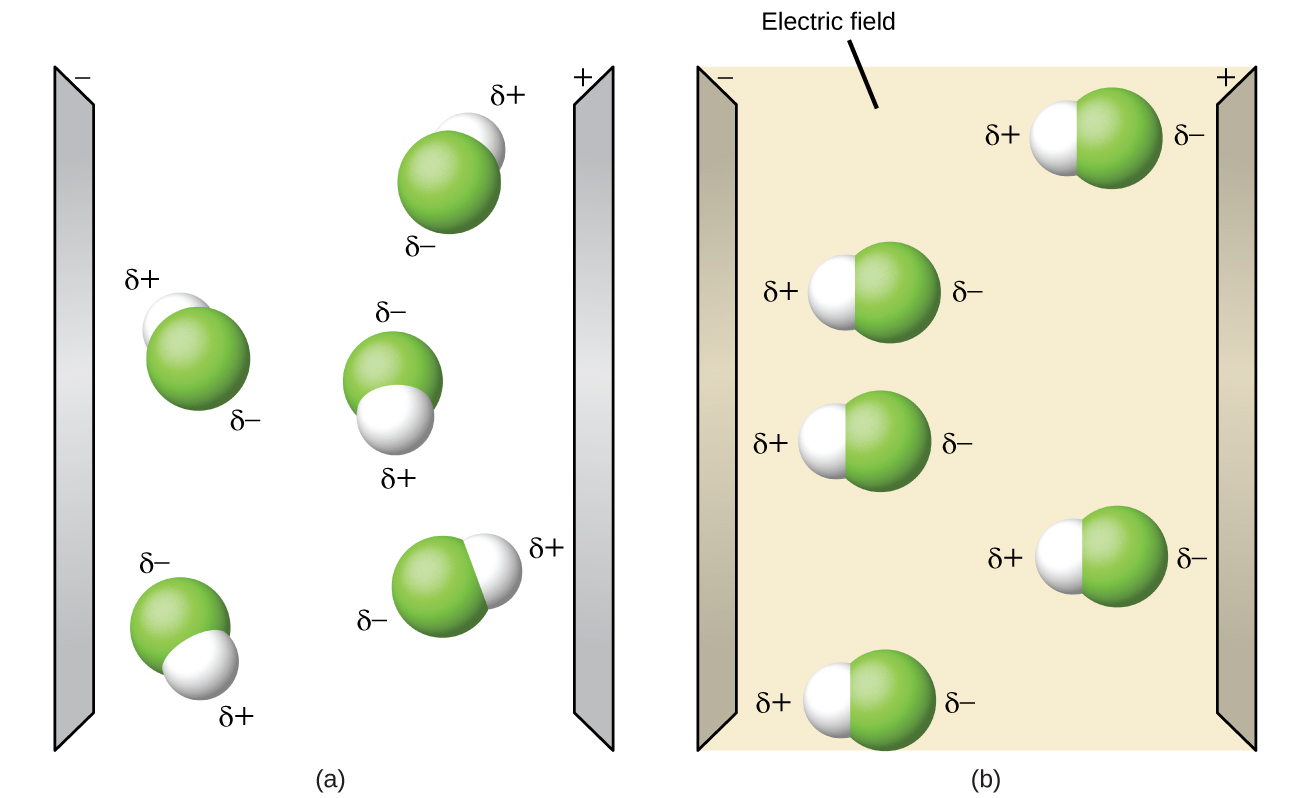
Properties Of Polar Molecules. Polar molecules tend to align when placed in an electric field with the positive end of the molecule oriented toward the negative plate and the negative end toward the positive plate figure pageindex 14. Polar molecules have a high boiling point melting point low vapour pressure and high surface tension. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the best shape of the molecule. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side.
 Properties Of Polar Molecules By Openstax Page 9 27 Jobilize From jobilize.com
Properties Of Polar Molecules By Openstax Page 9 27 Jobilize From jobilize.com
This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements. The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. Nonpolar molecules have a low boiling point melting point high vapour pressure and low surface tension. The molecule is not symmetric. We can use an electrically charged object to attract polar molecules but nonpolar molecules are not attracted. Water h2o is a polar bonded molecule.
The molecule is not symmetric.
Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond. This happens when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of each atom. Water h2o is a polar bonded molecule. Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is polar. 01 295 5546 0700sankore. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
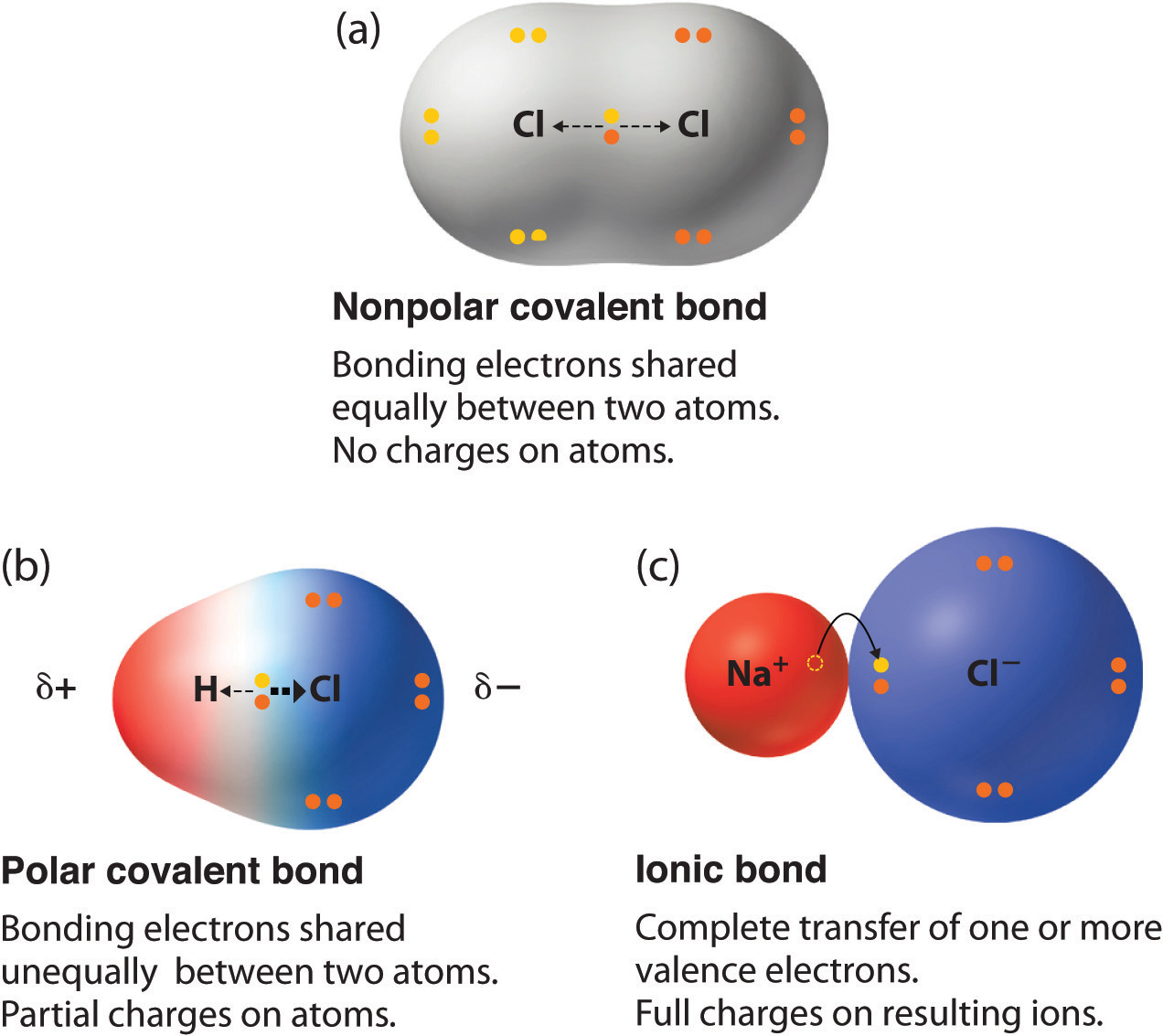
This happens when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of each atom. An extreme difference forms an ionic bond while a lesser difference forms a polar covalent bond. We can use an electrically charged object to attract polar molecules but nonpolar molecules are not attracted. Nonpolar molecules have a low boiling point melting point high vapour pressure and low surface tension. Hydrogen cyanide is polar.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is polar. An extreme difference forms an ionic bond while a lesser difference forms a polar covalent bond. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side. Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond. Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is polar.
 Source: pediaa.com
Source: pediaa.com
The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side. The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. 01 295 5546 0700sankore.
 Source: sciencenotes.org
Source: sciencenotes.org
The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is polar. Mon fri 08 00 17 00. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the best shape of the molecule. A dipole forms with part of the molecule carrying a slight positive charge and the other part carrying a slight negative charge.
 Source: itis.arezzo.it
Source: itis.arezzo.it
We can use an electrically charged object to attract polar molecules but nonpolar molecules are not attracted. Mon fri 08 00 17 00. This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements. Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond. Hydrogen cyanide is polar.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
This is not a symmetric molecule. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the best shape of the molecule. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond. Polar molecules have a high boiling point melting point low vapour pressure and high surface tension.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
We can use an electrically charged object to attract polar molecules but nonpolar molecules are not attracted. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements. Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond. 33b cameron road ikoyi lagos.
 Source: chemistry.elmhurst.edu
Source: chemistry.elmhurst.edu
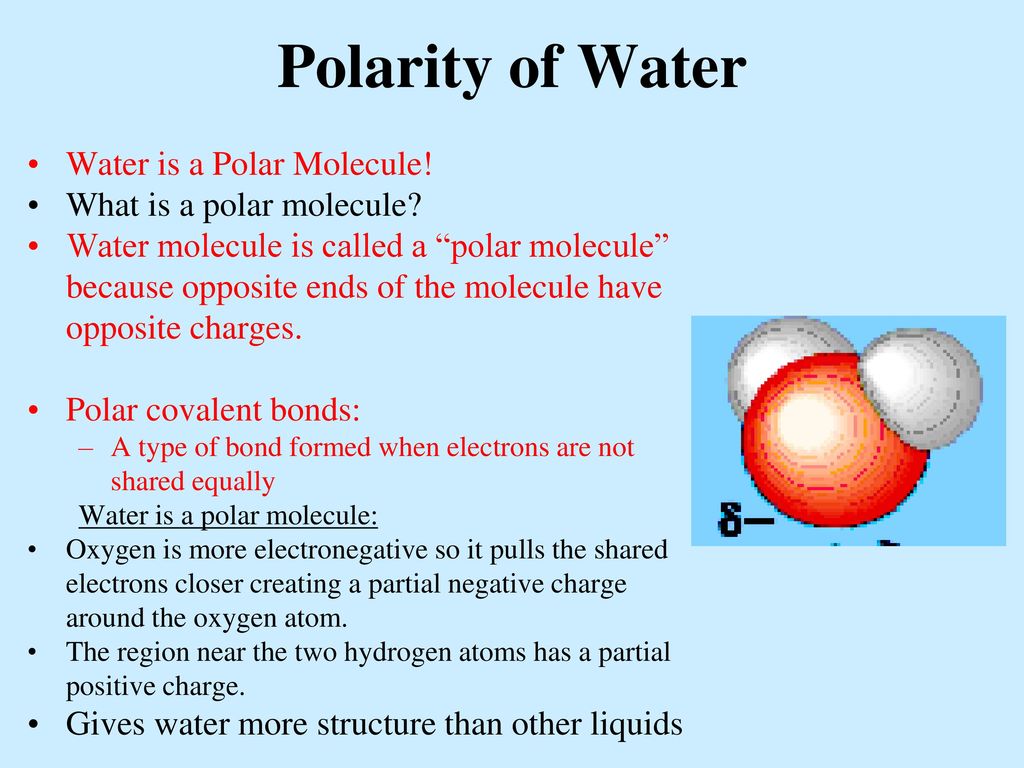
Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond. Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond. This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. The electronegativity amount of oxygen is 3 44 while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 2 20.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
Nonpolar molecules have a low boiling point melting point high vapour pressure and low surface tension. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side. The electronegativity amount of oxygen is 3 44 while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 2 20. Examples include water hf and chf 3. An extreme difference forms an ionic bond while a lesser difference forms a polar covalent bond.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the best shape of the molecule. This is not a symmetric molecule. Polar molecules interact through dipole dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. The molecule is not symmetric. This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
This occurs because of the differences in electronegativity between atoms of different elements. Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond. The electronegativity amount of oxygen is 3 44 while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 2 20. Any molecule with lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is polar. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Examples include water hf and chf 3. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the best shape of the molecule. Nonpolar molecules have a low boiling point melting point high vapour pressure and low surface tension. A polar molecule is characterized by the uneven distribution of the electrons that form the covalent bonds between each atom in the molecule resulting in a slightly positively charged side and a slightly negatively charged side. This is not a symmetric molecule.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension solubility and melting and boiling points. A dipole forms with part of the molecule carrying a slight positive charge and the other part carrying a slight negative charge. This is not a symmetric molecule. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. An extreme difference forms an ionic bond while a lesser difference forms a polar covalent bond.
 Source: jobilize.com
Source: jobilize.com
The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. The ce oh side is different from the other 3 ce h sides. Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond. Hydrogen cyanide is polar. Polar molecules have a high boiling point melting point low vapour pressure and high surface tension.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension solubility and melting and boiling points. A dipole forms with part of the molecule carrying a slight positive charge and the other part carrying a slight negative charge. This is not a symmetric molecule. Polar molecules occur when two atoms do not share electrons equally in a covalent bond. Polar covalent bond examples of molecules with polar covalent bond.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title properties of polar molecules by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





