Innermost layer of eye
Innermost Layer Of Eye. The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. The purpose of this layer is to receive the light from an object and convert it into electrical impulses that are then transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain. The retina is a nearly transparent sheet of tissue continuous with the optic nerve in the back of the eye and extending forward as the inner lining of the eyeball.
 Structure Of Human Eye And Its Working And Defects In Human Eye Scienceeasylearning From scienceeasylearning.wordpress.com
Structure Of Human Eye And Its Working And Defects In Human Eye Scienceeasylearning From scienceeasylearning.wordpress.com
The inner layer is also known as the retina or the sensory tunic. The inner layer of the eye is formed by the retina. Three layers of neural cells are present in them they are ganglion bipolar and photoreceptor cells. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. Rēte is the innermost light sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images.
The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye.
The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors. It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The innermost layer of the sun is called the core. The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors. The retina ends just behind the margin of the ciliary body. It covers the back two thirds of the inner eye and is composed 10 distinct layers each layer is made up of different cell types and serves a different function.
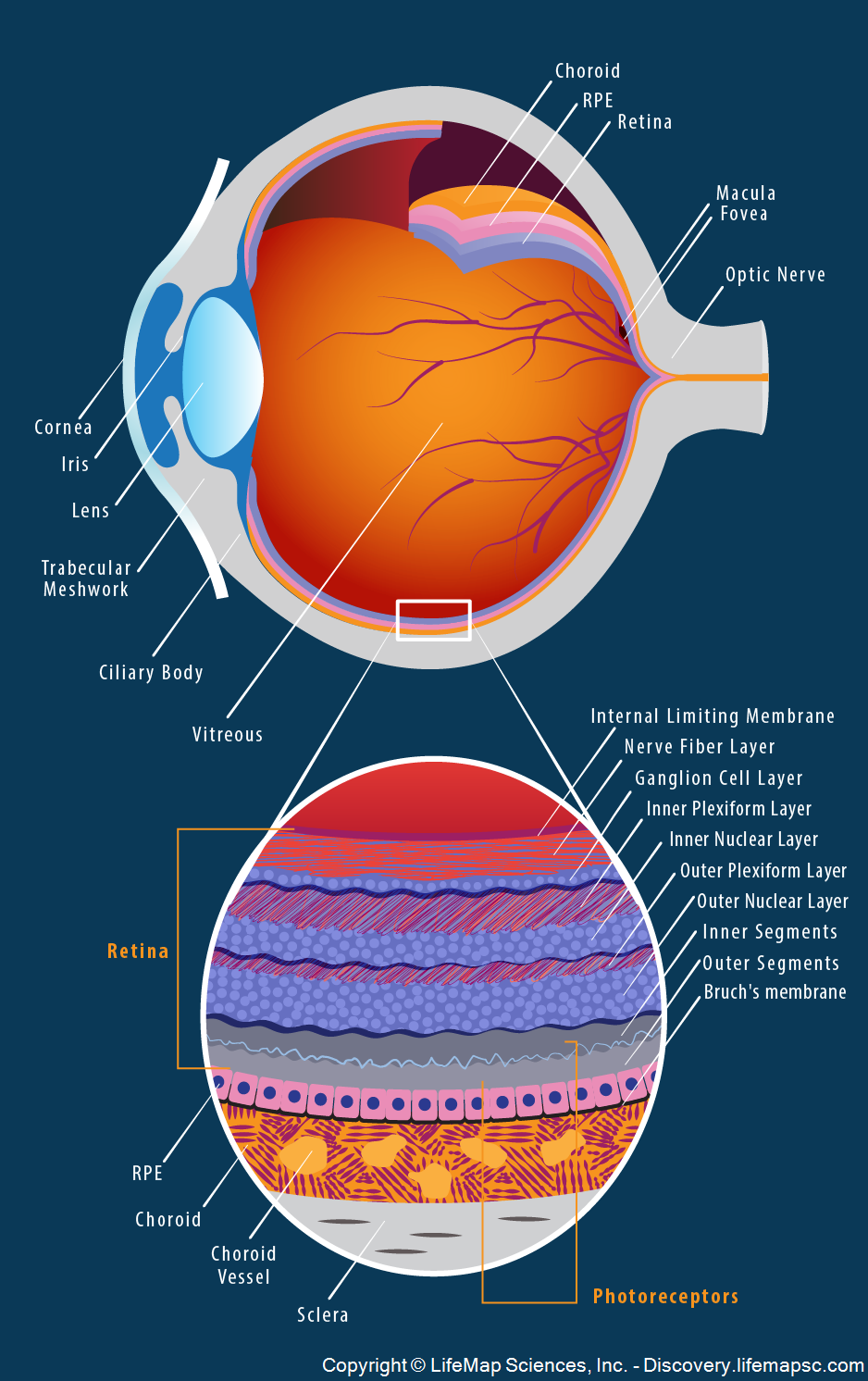 Source: discovery.lifemapsc.com
Source: discovery.lifemapsc.com
It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The innermost layer of the sun is called the core. The temperatures at the core are believed to be as high as 27 million degrees fahrenheit. The innermost layer of the eye is the retina. It consists of photorecetors rods and cons macula lutea fovea centralis and optic disc.
 Source: nicetoview.blogfa.com
Source: nicetoview.blogfa.com
The innermost layer of the sun is called the core. The retina exhibits significant degeneration in sanfilippo and is a tissue that can be monitored non invasively. The purpose of this layer is to receive the light from an object and convert it into electrical impulses that are then transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain. The innermost layer of the sun is called the core. Pigmented outer layer formed by a single layer of cells it is attached to the choroid and supports the choroid in absorbing light preventing scattering of light within the eyeball.
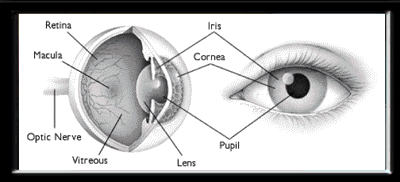 Source: ottawahospital.on.ca
Source: ottawahospital.on.ca
It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The inner layer of the eye is formed by the retina. It covers the back two thirds of the inner eye and is composed 10 distinct layers each layer is made up of different cell types and serves a different function. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. It is the innermost layer of the eye.
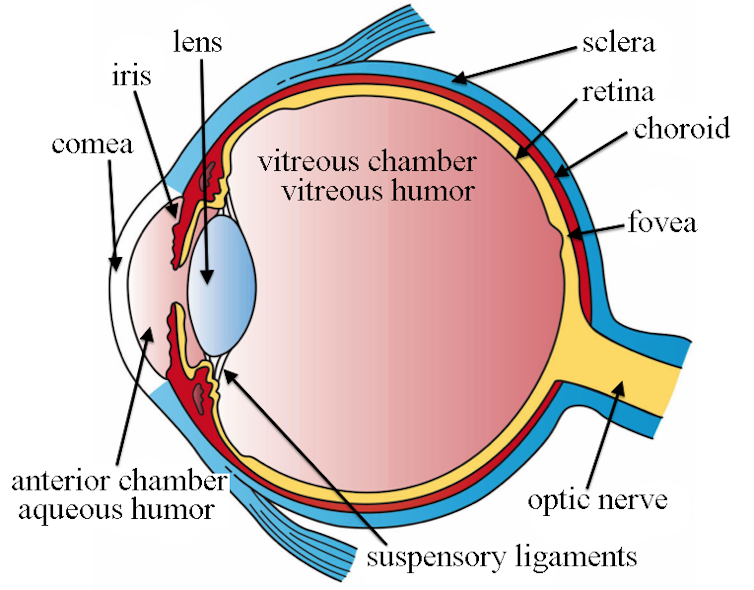 Source: theconversation.com
Source: theconversation.com
It is light sensitive and acts as a film of a camera. It is the innermost layer of the eye. Rēte is the innermost light sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. Three layers of neural cells are present in them they are ganglion bipolar and photoreceptor cells. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images.
 Source: scienceeasylearning.wordpress.com
Source: scienceeasylearning.wordpress.com
The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors. It consists of photorecetors rods and cons macula lutea fovea centralis and optic disc. The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images. The retina is a nearly transparent sheet of tissue continuous with the optic nerve in the back of the eye and extending forward as the inner lining of the eyeball.
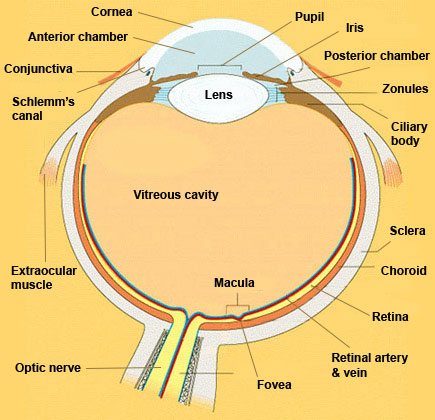 Source: kellogg.umich.edu
Source: kellogg.umich.edu
Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images. The optics of the eye create a focused two dimensional image of the visual world on the retina which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception. It consists of photorecetors rods and cons macula lutea fovea centralis and optic disc. The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye.
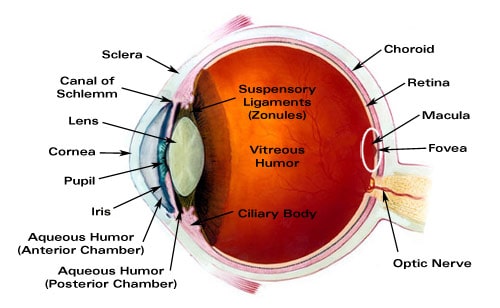 Source: laramyk.com
Source: laramyk.com
The innermost layer of the sun is called the core. It is light sensitive and acts as a film of a camera. It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The retina exhibits significant degeneration in sanfilippo and is a tissue that can be monitored non invasively. The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors.
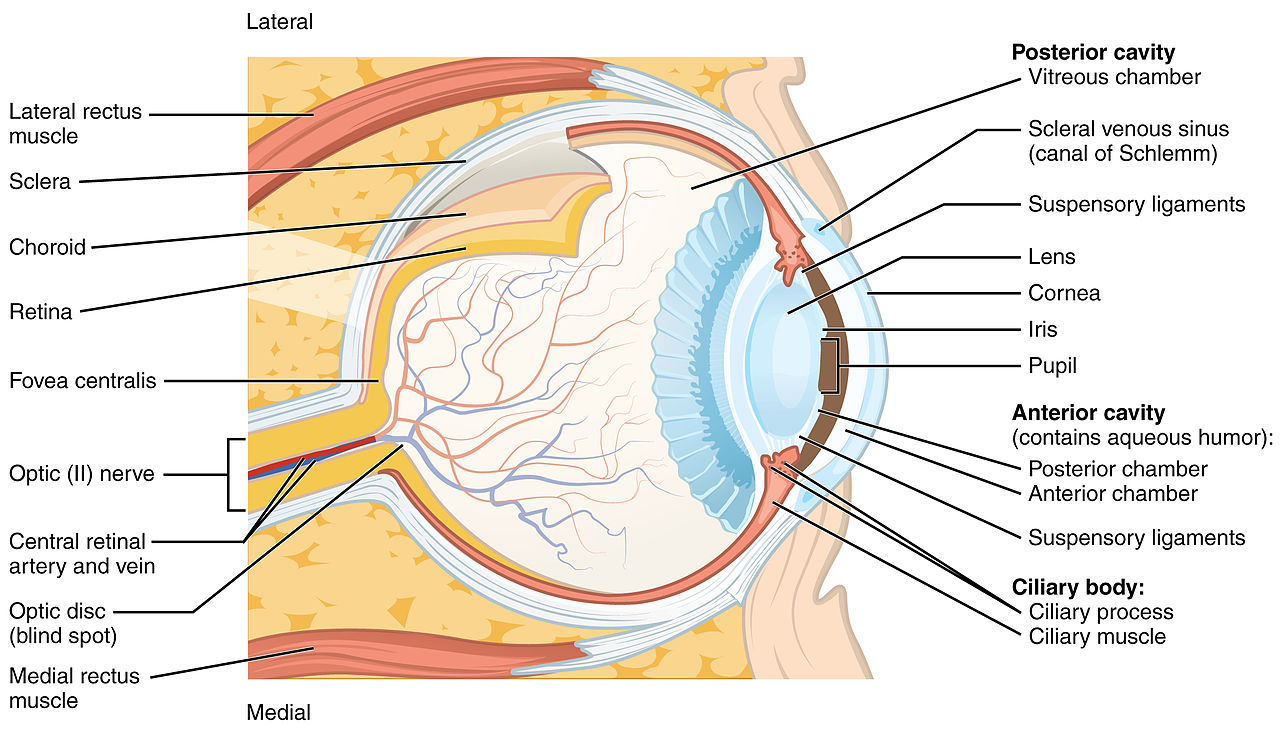 Source: content.byui.edu
Source: content.byui.edu
The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images. It covers the back two thirds of the inner eye and is composed 10 distinct layers each layer is made up of different cell types and serves a different function. Three layers of neural cells are present in them they are ganglion bipolar and photoreceptor cells. The inner layer of the wall of the eye consists of the retina which contains the visual receptor cells photoreceptors. The inner layer of the eye is formed by the retina.
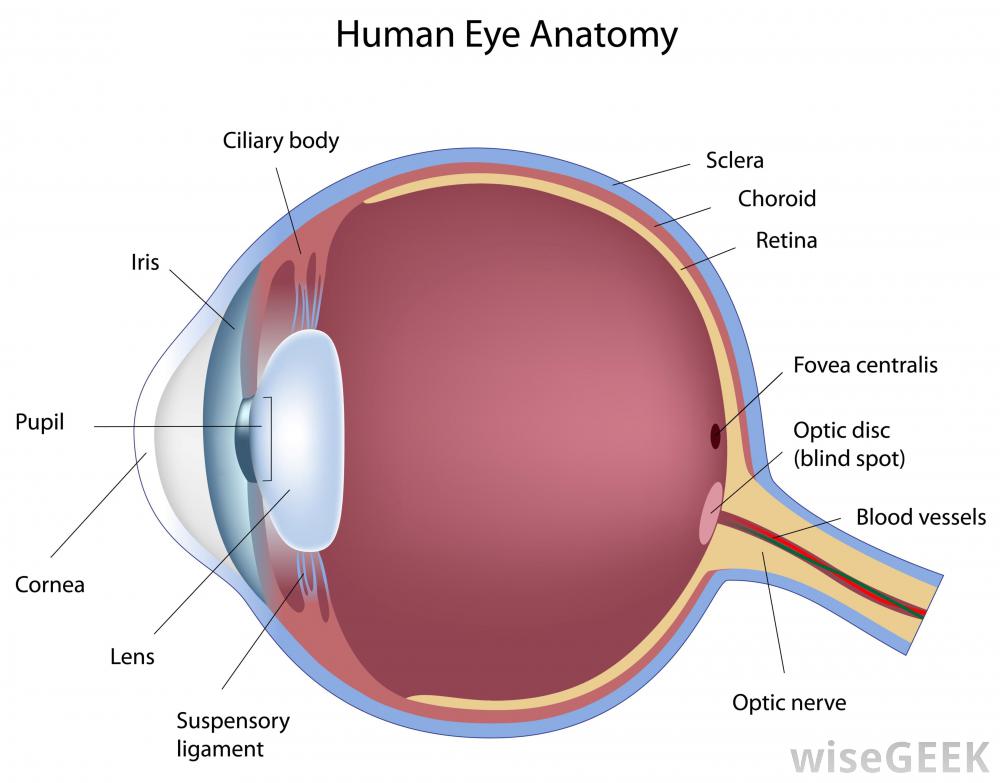 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
Rēte is the innermost light sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. It is the innermost layer of the eye. The retina exhibits significant degeneration in sanfilippo and is a tissue that can be monitored non invasively. The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye. The retina ends just behind the margin of the ciliary body.
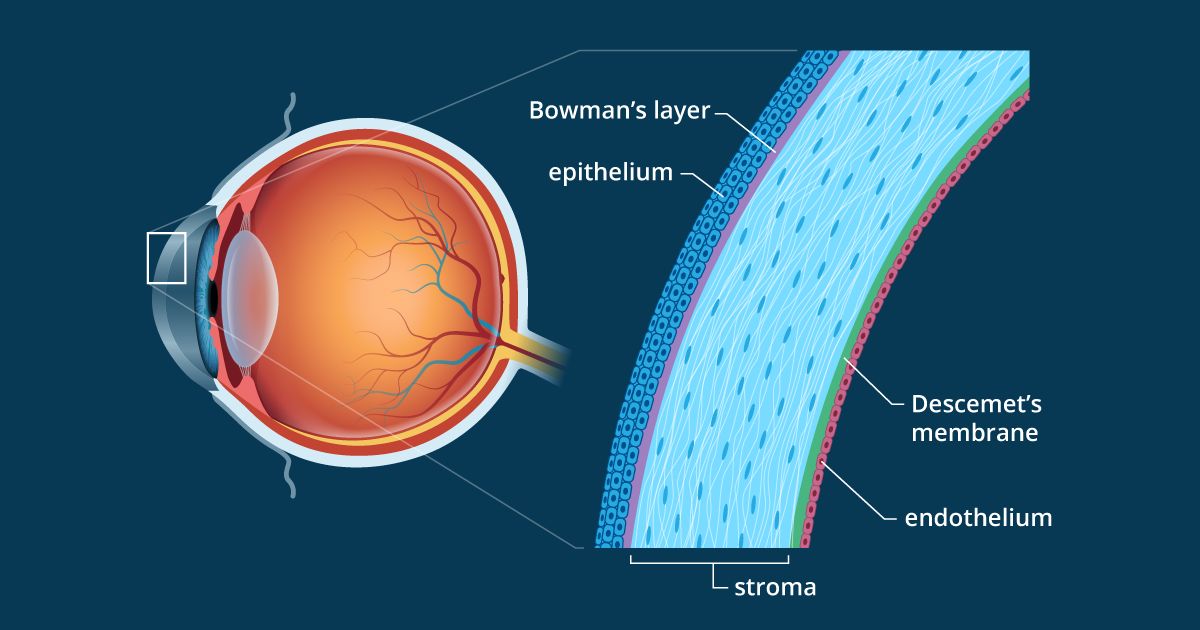 Source: allaboutvision.com
Source: allaboutvision.com
The inner layer is also known as the retina or the sensory tunic. The purpose of this layer is to receive the light from an object and convert it into electrical impulses that are then transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain. It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. It consists of photorecetors rods and cons macula lutea fovea centralis and optic disc. It is the innermost layer of the eye.
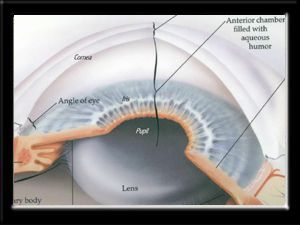 Source: ottawahospital.on.ca
Source: ottawahospital.on.ca
The retina ends just behind the margin of the ciliary body. The retina is a nearly transparent sheet of tissue continuous with the optic nerve in the back of the eye and extending forward as the inner lining of the eyeball. The inner layer of the eye is formed by the retina. Three layers of neural cells are present in them they are ganglion bipolar and photoreceptor cells. The retina from latin.
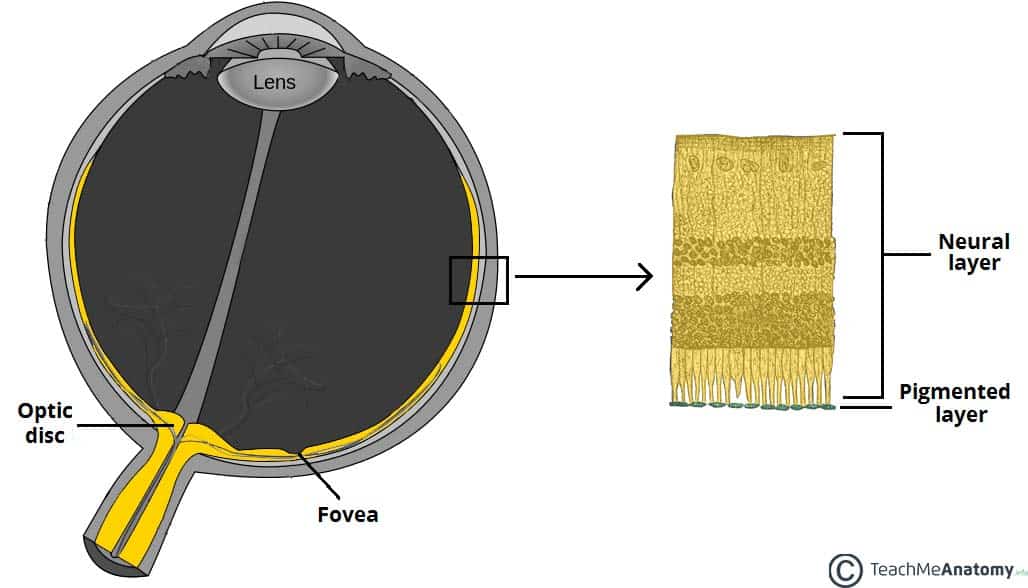 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Its light detecting component the retina is composed of two layers. The retina ends just behind the margin of the ciliary body. The innermost layer of the eye is the retina. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. The retina exhibits significant degeneration in sanfilippo and is a tissue that can be monitored non invasively. The optics of the eye create a focused two dimensional image of the visual world on the retina which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception. It is the innermost layer of the eye.
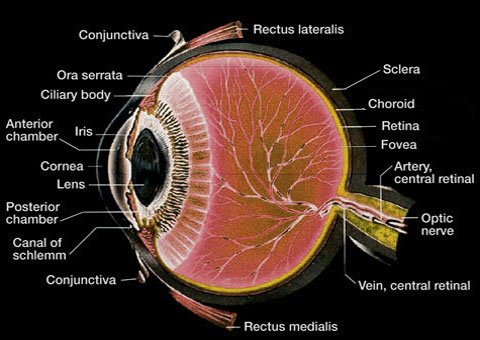 Source: histology-world.com
Source: histology-world.com
The optics of the eye create a focused two dimensional image of the visual world on the retina which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception. Moreover in many neurological disorders retinal lesions parallel or even precedes. The inner layer is also known as the retina or the sensory tunic. The retina is the innermost layer of the eye that receives light and sends that information to the brain which then transforms it into images. It is light sensitive and acts as a film of a camera.
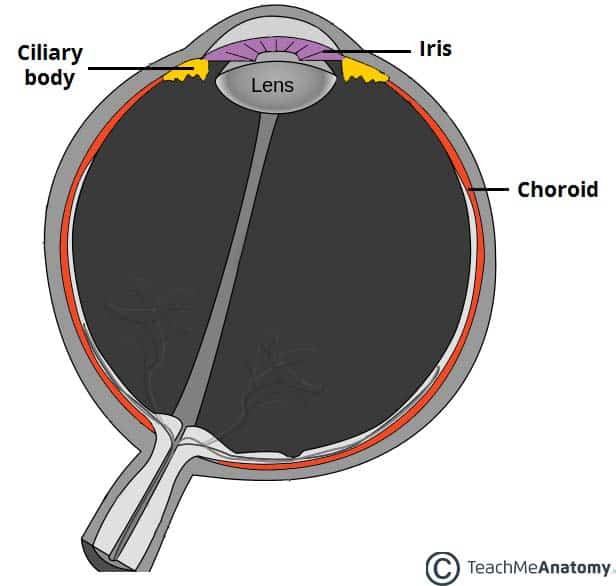 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The retina is a complex multilayered tissue at the back of the eye. Pigmented outer layer formed by a single layer of cells it is attached to the choroid and supports the choroid in absorbing light preventing scattering of light within the eyeball. It converts the image into electrical nerve impulses for the visual perception by the brain. The purpose of this layer is to receive the light from an object and convert it into electrical impulses that are then transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title innermost layer of eye by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





