Alkali metals melting point
Alkali Metals Melting Point. An alloy of 41 caesium 47 sodium and 12 potassium has the lowest known melting point of any metal or alloy 78 c. They have low melting points increasing up the group from 28 c for cs to 180 c for li whereas typical metals have much higher melting points such as iron which melts at 1 540 c they are. The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium. When any of the group 1 metals is melted the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached.
 Alkali Metal Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
Alkali Metal Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
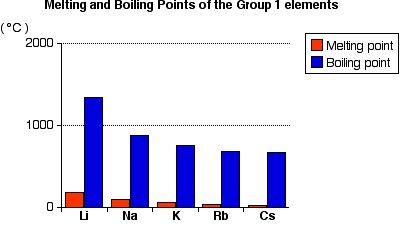
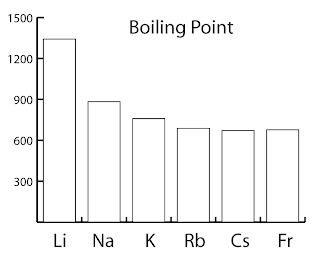
Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides. The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase. These elements are also excellent conductors of heat and electricity. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements. Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1. Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f.
Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides.
Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1. Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides. Compounds with the group 13 elements. Trends in melting and boiling points. An alloy of 41 caesium 47 sodium and 12 potassium has the lowest known melting point of any metal or alloy 78 c.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
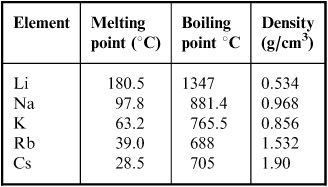
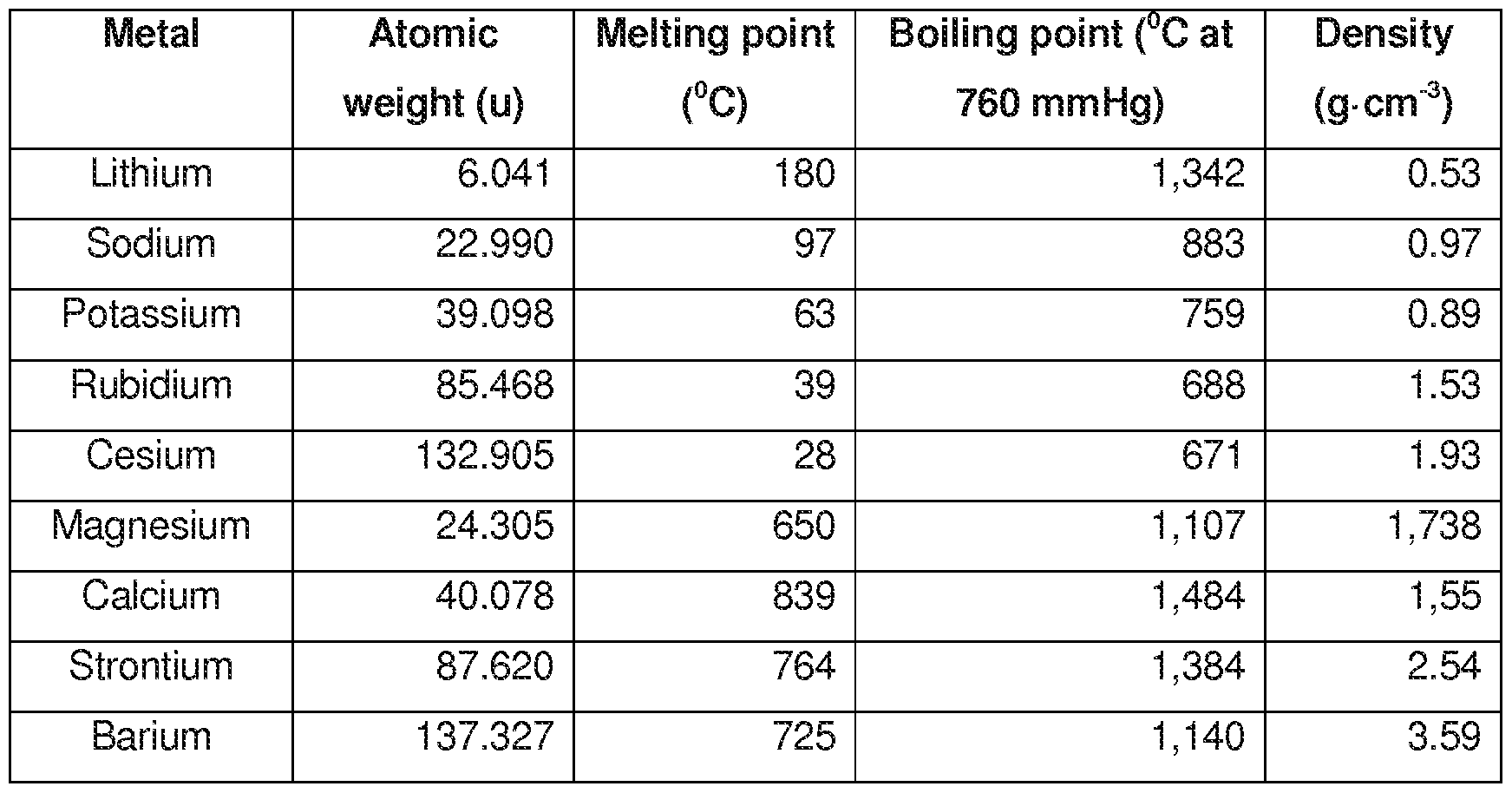
The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase. The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. The increasing atomic radius means weaker forces between the atoms and so a lower melting and boiling point. When any of the group 1 metals is melted the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. The alkali metals are very reactive and so are usually found in compounds with other elements such as salt sodium chloride nacl and potassium chloride kcl. Trends in melting and boiling points.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com
Compounds with the group 13 elements. Both the melting and boiling points decrease down the group. Trends in melting and boiling points. Compounds with the group 13 elements. When any of the group 1 metals is melted the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium. Compounds with the group 13 elements. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. When any of the group 1 metals is melted the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached. They have low melting points increasing up the group from 28 c for cs to 180 c for li whereas typical metals have much higher melting points such as iron which melts at 1 540 c they are.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. Trends in melting and boiling points. These elements are also excellent conductors of heat and electricity. Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1.
 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. The increasing atomic radius means weaker forces between the atoms and so a lower melting and boiling point. When any of the group 1 metals is melted the metallic bond is weakened enough for the atoms to move more freely and is broken completely when the boiling point is reached. For the same alkali metal the melting points decrease in the order with the increase in the size of halides ion. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. Compounds with the group 13 elements. For the same alkali metal the melting points decrease in the order with the increase in the size of halides ion. The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium.
 Source: sukachem.blogspot.com
Source: sukachem.blogspot.com
Alkali metals are soft. The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase. Alkali metals are soft. The table shows the melting points of five alkali metals. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements. Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides. The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium. Both the melting and boiling points decrease down the group. The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They have low melting points increasing up the group from 28 c for cs to 180 c for li whereas typical metals have much higher melting points such as iron which melts at 1 540 c they are. The melting points of the alkali metals as a group are lower than those of any other nongaseous group of the periodic table ranging between 179 c 354 f for lithium and 28 5 c 83 3 f for cesium. The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase. Trends in melting and boiling points. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements.
 Source: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
Source: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
These elements are also excellent conductors of heat and electricity. Both the melting and boiling points decrease down the group. Fluorides chlorides bromides iodides for the same halide ion melting points decreases with the increasing size of the metal but lithium halides being covalent have lower melting point than corresponding sodium halides. The alkali metals are very reactive and so are usually found in compounds with other elements such as salt sodium chloride nacl and potassium chloride kcl. An alloy of 41 caesium 47 sodium and 12 potassium has the lowest known melting point of any metal or alloy 78 c.
 Source: physicalscience.pbworks.com
Source: physicalscience.pbworks.com
The increasing atomic radius means weaker forces between the atoms and so a lower melting and boiling point. The alkali metals have low melting points. Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1. Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. They have low melting points increasing up the group from 28 c for cs to 180 c for li whereas typical metals have much higher melting points such as iron which melts at 1 540 c they are.
 Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Source: chemistry.stackexchange.com
Lithium melts at 180 5 c 356 9 f. Both the melting and boiling points decrease down the group. Alkali metals are soft. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements. These elements are also excellent conductors of heat and electricity.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Both the melting and boiling points decrease down the group. The increasing atomic radius means weaker forces between the atoms and so a lower melting and boiling point. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements. The decrease in melting and boiling points down the group can be explained by the additional shell being added to the previous element causing the atomic radius to increase. Alkali metals are soft.
 Source: acsdohachemistry10b.wordpress.com
Source: acsdohachemistry10b.wordpress.com
Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. The figure above shows melting and boiling points of the group 1 elements. Cesium melts at just 28 4 c 83 1 f. An alloy of 41 caesium 47 sodium and 12 potassium has the lowest known melting point of any metal or alloy 78 c. Use this information to describe how the melting point changes in group 1.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title alkali metals melting point by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.